What is bid and ask price in forex
At its core, the forex market is all about the exchange of one currency for another. Each currency pair, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY, comprises two prices: the bid price and the ask price. The bid price represents the maximum amount a buyer is willing to pay for a specific currency pair, while the ask price is the minimum amount at which a seller is willing to part with it. These prices are in constant flux, moving up and down, as they are driven by the forces of supply and demand.
Understanding bid and ask prices is not merely a matter of academic curiosity; it's the bedrock upon which profitable forex trading is built. These prices determine the entry and exit points for trades, influencing the profitability of each transaction. A firm grasp of bid and ask prices empowers traders to make informed decisions, manage risks, and seize opportunities with confidence.
Understanding forex market basics
The forex market, short for the foreign exchange market, is a global financial marketplace where currencies are traded. It's the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion, dwarfing the stock and bond markets. Unlike centralized exchanges, the forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, thanks to its decentralized nature.
Traders in the forex market participate to profit from the fluctuations in exchange rates between different currencies. These fluctuations are driven by a myriad of factors, including economic data releases, geopolitical events, interest rate differentials, and market sentiment. This constant ebb and flow of currencies creates opportunities for traders to buy and sell, aiming to capitalize on price movements.
In forex trading, currencies are quoted in pairs, like EUR/USD or USD/JPY. The first currency in the pair is the base currency, and the second is the quote currency. The exchange rate tells you how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. For example, if the EUR/USD pair is quoted at 1.2000, it means that 1 Euro can be exchanged for 1.20 US Dollars.
Bid price: the buying price
The bid price in forex represents the highest price at which a trader is willing to buy a particular currency pair at any given moment. It's the essential component of every forex trade as it determines the buying price. The bid price is crucial because it represents the point at which traders can enter a long (buy) position in the market. It signifies the demand for the base currency relative to the quote currency. Understanding the bid price helps traders gauge market sentiment and potential buying opportunities.
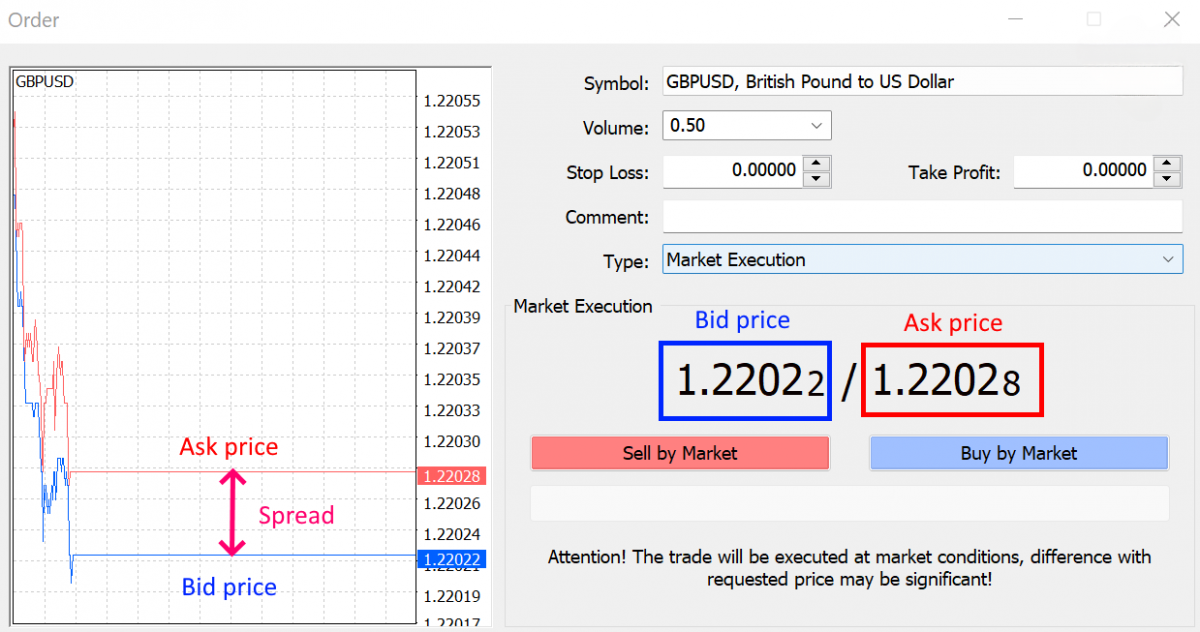
In a currency pair like EUR/USD, the bid price is typically shown on the left side of the quote. For instance, if the EUR/USD pair is quoted at 1.2000/1.2005, the bid price is 1.2000. This means that you can sell 1 Euro for 1.2000 US Dollars. The bid price is what brokers are willing to pay to purchase the base currency from traders.
Let's consider an example: If you believe that the EUR/USD pair will rise in value, you might place a market order to buy it. Your broker would execute the order at the current bid price, let's say 1.2000. This means you'll enter the trade with a buying price of 1.2000. If the pair appreciates, you can sell it later at a higher ask price, realizing a profit.
Ask price: the selling price
The ask price in forex signifies the lowest price at which a trader is willing to sell a particular currency pair at any given moment. It's the counterpart to the bid price and is essential for determining the selling price in forex trading. The ask price represents the supply of the base currency relative to the quote currency. Understanding the ask price is vital as it determines the price at which traders can exit long (sell) positions or enter short (sell) positions in the market.
In a currency pair such as EUR/USD, the ask price is typically displayed on the right side of the quote. For example, if the EUR/USD pair is quoted at 1.2000/1.2005, the ask price is 1.2005. This means you can buy 1 Euro for 1.2005 US Dollars. The ask price is the price at which brokers are willing to sell the base currency to traders.
Consider this scenario: If you anticipate that the USD/JPY pair will decline in value, you may decide to sell it. Your broker would execute the trade at the current ask price, let's say 110.50. This means you would enter the trade with a selling price of 110.50. If the pair indeed drops in value, you can buy it back later at a lower bid price, thus realizing a profit.
The bid-ask spread
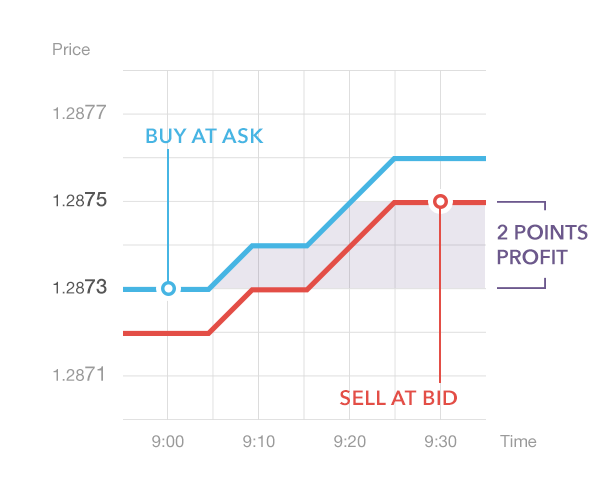
The bid-ask spread in forex is the difference between the bid price (the buying price) and the ask price (the selling price) of a currency pair. It represents the cost of executing a trade and serves as a measure of liquidity in the market. The spread matters because it directly affects a trader's profitability. When you buy a currency pair, you do so at the ask price, and when you sell, you do it at the bid price. The difference between these prices, the spread, is the amount that the market must move in your favour for your trade to become profitable. A narrower spread is generally more favourable for traders, as it reduces the cost of trading.
Several factors can influence the size of the bid-ask spread in the forex market. These include market volatility, liquidity, and trading hours. During times of high volatility, such as major economic announcements or geopolitical events, spreads tend to widen as uncertainty increases. Similarly, when liquidity is low, such as during after-hours trading, spreads can be wider as there are fewer market participants.
For instance, consider the EUR/USD pair. During normal trading hours, the spread might be as tight as 1-2 pips (percentage in point). However, during periods of high volatility, such as when a central bank makes a sudden interest rate announcement, the spread can widen to 10 pips or more. Traders must be aware of these fluctuations and factor in the spread when entering and exiting trades to ensure it aligns with their trading strategy and risk tolerance.
The role of bid and ask prices in forex trading
In the forex market, bid and ask prices are inextricably linked and play a crucial role in facilitating trade. When traders buy a currency pair, they do so at the ask price, which represents the price at which sellers are willing to sell. Conversely, when they sell, they do so at the bid price, the point at which buyers are willing to purchase. This interplay between bid and ask prices creates the liquidity that makes forex trading possible. The narrower the bid-ask spread, the more liquid the market.
Traders use bid and ask prices as key indicators to formulate their trading strategies. For instance, if a trader believes that the EUR/USD pair will appreciate, they will look to enter a long position at the ask price, anticipating a future sale at a higher bid price. Conversely, if they anticipate depreciation, they may enter a short position at the bid price.
Monitor market conditions: Keep an eye on market conditions and spreads, especially during volatile times. Tight spreads are generally more favourable for traders.
Use limit orders: Consider using limit orders to enter trades at specific price levels. This allows you to specify your desired entry or exit points, ensuring you don't get caught up in unexpected price fluctuations.
Stay informed: Be aware of economic events, news releases, and geopolitical developments that can impact bid and ask prices. These factors can lead to rapid price movements and changes in spreads.
Practice risk management: Always calculate the spread and potential costs before entering a trade. Risk management is vital to protect your capital.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bid and ask prices are the lifeblood of the forex market. As we've discovered, bid prices represent buying opportunities, while ask prices dictate selling points. The bid-ask spread, a measure of market liquidity and trading cost, acts as a constant companion in every trade.
Understanding bid and ask prices is not merely a luxury; it is a necessity for every forex trader. It allows you to make well-informed decisions, seize opportunities, and protect your hard-earned capital. Whether you are a day trader, a swing trader, or a long-term investor, these prices hold the key to unlocking your trading potential.
The forex market is a dynamic and ever-evolving ecosystem. To thrive in it, continuously educate yourself, stay updated on market developments, and practice disciplined risk management. Consider leveraging demo accounts to hone your skills without risking real capital.
The forex market offers boundless opportunities for those who are dedicated to honing their craft and making informed decisions in this ever-changing landscape. So, keep learning, keep practising, and may your understanding of bid and ask prices pave the way for a successful and rewarding forex trading career.


