Martingale forex strategy
The Martingale Forex strategy is a high-risk, high-reward trading approach that originated in 18th-century France, initially applied to gambling. Over time, it found its way into financial markets, including forex trading, where it gained traction due to its potential for quick recovery of losses. The central concept of the Martingale strategy is doubling the size of a trade after each loss, with the assumption that eventually, a winning trade will occur, offsetting all previous losses and providing a profit.
In the context of forex, the strategy involves increasing position sizes on consecutive losing trades, betting on the eventual reversal of the currency pair’s movement. While this method can be lucrative in theory, its execution requires a large amount of capital to withstand extended losing streaks, making it more suitable for experienced traders with a robust risk tolerance.
Despite its popularity, the Martingale strategy is controversial due to the substantial risk involved. If the market trends consistently against the trader's position, it can lead to large drawdowns and the potential depletion of trading accounts.
How the Martingale strategy works in forex trading
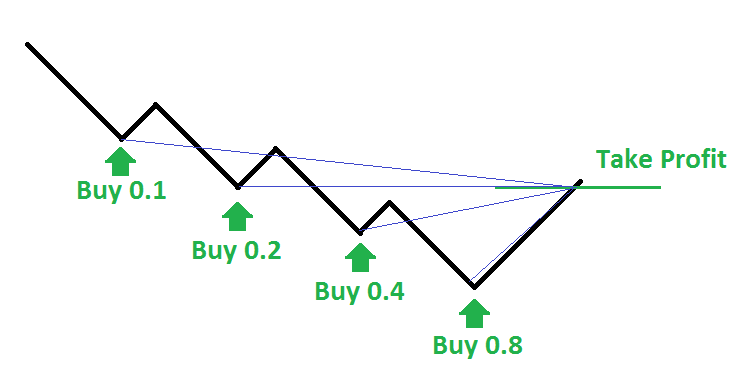
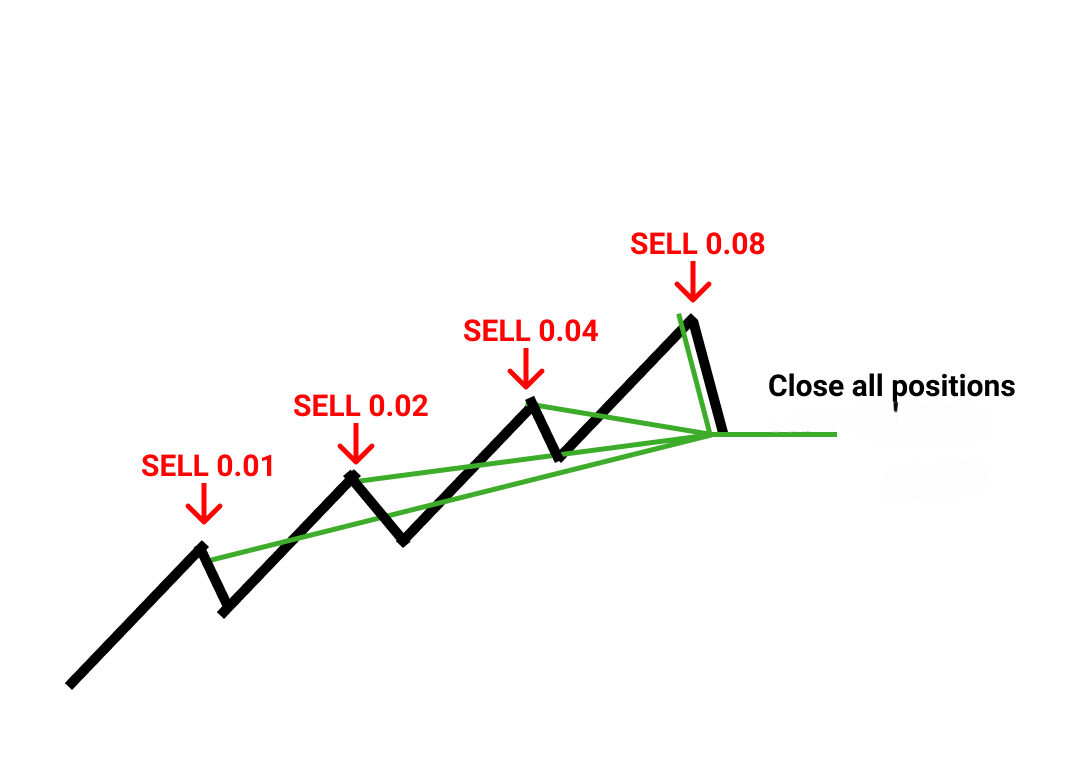
The Martingale strategy in forex trading operates on a simple yet risky principle: doubling the position size after every losing trade. The core assumption is that eventually, a winning trade will occur, allowing the trader to recover previous losses and achieve a small profit. For example, if a trader starts with a $100 buy position on EUR/USD and the market moves against them, they would double their next position to $200, then $400, and so on until the market reverses in their favor. Once a winning trade occurs, the profits from the larger position size would cover the accumulated losses.
In forex, this approach is typically used in range-bound or consolidating markets where prices fluctuate within a defined range. However, it requires significant capital to sustain multiple losing trades, as the size of each new position increases exponentially. Traders also need to be aware of margin requirements and the risk of margin calls, which can deplete an account if a prolonged trend moves against the positions.
While the Martingale strategy might appeal to traders seeking quick recoveries from losses, it’s crucial to recognize the dangers of compounding risk. Without sufficient capital and risk management, this strategy can lead to significant financial loss, especially in trending or volatile markets.
Advantages of using the Martingale strategy in forex
One of the primary advantages of the Martingale strategy in forex trading is its potential for high win rates. Since the strategy involves doubling down on losing trades, the first winning trade should, in theory, cover all previous losses and generate a small profit. This makes it appealing in markets that tend to revert to the mean or stay within a particular price range. Traders operating in range-bound markets can benefit from this, especially during periods of low volatility, where significant price swings are less likely to occur.
Another advantage is the simplicity of the strategy. The Martingale approach follows a straightforward rule: increase position size after each loss. This simplicity makes it accessible to many traders who may not have the time or inclination to develop complex trading systems. Additionally, in short-term trading, especially in low-volatility forex pairs like EUR/CHF or USD/JPY, the Martingale strategy can sometimes work effectively, offering the potential to recover losses relatively quickly.
Disadvantages and risks of the Martingale strategy
The Martingale strategy carries significant risks, with the most notable being its potential for unlimited losses. Because the strategy relies on doubling the position size after each loss, the capital required grows exponentially with each subsequent losing trade. For example, a losing streak of just five trades can lead to a position size that is 32 times larger than the initial trade, quickly depleting an account without a substantial cash reserve.
Another major risk is vulnerability to long losing streaks. In a trending market, where prices move consistently in one direction without reversal, the Martingale strategy can fail catastrophically. If a trader keeps increasing position sizes in a trend that continues against them, they may encounter massive drawdowns or complete account liquidation.
Margin calls also present a critical risk with this strategy. When a trader's account runs out of available margin due to oversized positions, the broker may issue a margin call, forcing the trader to deposit more funds or liquidate positions at a loss. This can happen abruptly if the market moves heavily against the trader.
In worst-case scenarios, such as during sharp market trends or unexpected economic events, a prolonged losing streak can wipe out even well-funded trading accounts. The Martingale forex strategy, while enticing, requires careful risk management to avoid total loss.
Martingale strategy in practice: tips for implementation
To use the Martingale strategy effectively in forex trading, it’s crucial to adopt a disciplined approach that minimizes risk. One of the key recommendations is to choose currency pairs with lower volatility. Pairs like EUR/CHF or USD/JPY tend to experience smaller price swings, which can reduce the likelihood of large losses and make the strategy more manageable. By focusing on stable currency pairs, traders can mitigate the chances of facing extended losing streaks that could rapidly deplete their capital.
Limiting the number of consecutive trades is another essential risk management tactic. Instead of allowing the Martingale strategy to run indefinitely, traders should establish a predefined cut-off point, whether that’s a maximum number of trades or a total loss threshold. This helps protect the account from being wiped out by an adverse market movement.
Setting maximum loss limits is also critical. Traders can define a stop-loss level that, when triggered, closes all open positions to prevent further losses. This tactic ensures that traders don’t get caught in an uncontrollable losing streak. Additionally, managing position sizing is key to survival. Starting with small, manageable trade sizes allows for flexibility and reduces the risk of over-leveraging.
Alternatives to the Martingale strategy
While the Martingale strategy can deliver quick recoveries from losses, its high-risk nature makes it unsuitable for many traders. Fortunately, there are safer risk management strategies that can be more sustainable in the long term. One common alternative is the Anti-Martingale approach, which reverses the logic of the Martingale strategy. Instead of increasing position sizes after a loss, traders reduce their exposure following a losing trade and increase it after a winning trade. This approach protects capital during losing streaks while allowing traders to capitalize on winning trends without the exponential risk.
Hedging strategies also offer a way to reduce risk. By opening positions that counterbalance each other, traders can mitigate potential losses. For example, if a trader holds a long position on EUR/USD, they might open a short position on a correlated currency pair to offset potential downturns. This allows traders to manage risk while staying active in the market.
Diversification is another powerful strategy for reducing risk. Instead of focusing on a single currency pair, traders can spread their investments across multiple pairs or markets, decreasing the impact of a losing position. Additionally, the use of stop-loss orders is crucial for risk management, as they automatically close a trade when a predefined loss level is reached, preventing catastrophic losses.
Examples of Martingale in forex trading
In the world of forex trading, there have been both successful and unsuccessful instances of traders using the Martingale strategy. One notable example of success occurred with a retail trader during a period of low volatility in the EUR/CHF pair. By implementing the Martingale strategy in a range-bound market, the trader was able to recover losses after several consecutive losing trades, ultimately turning a small profit once the market reversed. However, this success was heavily reliant on stable market conditions, and the trader had ample capital to withstand temporary drawdowns.
On the other hand, the limitations of the Martingale strategy are starkly illustrated in the case of the 2015 Swiss franc shock. Several traders using Martingale were caught off-guard when the Swiss National Bank unexpectedly removed the CHF peg to the euro, causing a massive spike in the Swiss franc's value. Those employing Martingale, expecting the market to revert to normal levels, found themselves facing catastrophic losses as the currency continued to trend in one direction. In some cases, entire trading accounts were wiped out.
Conclusion
The Martingale strategy holds a unique place in forex trading, offering the potential for rapid recovery from losses under the right market conditions. However, its high-risk nature makes it a double-edged sword. While theoretically sound, the strategy's success depends on a trader’s ability to withstand extended losing streaks and manage the exponential increase in trade sizes. For this reason, the Martingale strategy is best suited for traders with deep capital reserves and a strong tolerance for risk.
Risk management is critical for any trader considering this approach. Without carefully defined limits, the Martingale strategy can lead to catastrophic losses, especially in trending markets where prices continue moving in one direction. Traders must adopt strict safeguards, such as setting maximum loss thresholds, limiting consecutive trades, and focusing on currency pairs with lower volatility, to mitigate these risks.
For retail traders, the Martingale strategy can be viable, but it requires careful consideration. Many retail traders may lack the large capital needed to execute this strategy safely over the long term. As a result, the strategy may be more appropriate for experienced traders with robust risk management practices in place. Ultimately, success with the Martingale strategy hinges on understanding the associated risks and tailoring it to fit individual trading styles and market conditions.


