Forex algorithmic trading strategies
Algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading or automated trading, is a sophisticated method of executing trades in the Forex market. It involves the use of computer programs and algorithms to analyse market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute orders with incredible speed and precision. This approach has gained immense popularity among Forex traders for its ability to remove emotional biases and make split-second decisions based on predetermined criteria.
In the rapid world of currency trading, algorithmic strategies have become indispensable tools for both individual and institutional traders. The importance of these strategies lies in their capacity to navigate the complexities of the Forex market, which operates 24 hours a day and is influenced by numerous variables, such as economic data, geopolitical events, and market sentiment.
Understanding algorithmic trading
Algorithmic trading, often referred to as algo trading, is a trading strategy that relies on computer algorithms to execute a series of pre-defined instructions automatically. These algorithms are designed to analyse vast amounts of market data, including price movements, trading volumes, and various technical indicators, to make informed trading decisions. In the context of the Forex market, algorithmic trading involves the use of these algorithms to buy or sell currency pairs at optimal prices and times.
The concept of algorithmic trading dates back to the early 1970s when electronic trading platforms first emerged. However, it was in the 1990s that algorithmic trading gained significant traction in the Forex market. With the advent of high-speed internet and advanced computing technologies, traders and financial institutions began developing sophisticated algorithms to gain a competitive edge.
Today, algorithmic trading in the Forex market has evolved immensely. It has become an integral part of the financial market, dominating trading volumes.
Key components of algorithmic trading
At the heart of algorithmic trading lies the meticulous analysis and collection of data. Traders utilize historical and real-time market data, including price movements, trading volumes, economic indicators, and news feeds, to make informed decisions. The quality and granularity of data significantly impact the effectiveness of trading algorithms. Data analysis not only identifies patterns and trends but also provides the foundation for generating trading signals.
Trading signals and indicators are the building blocks of algorithmic trading strategies. These are mathematical formulas or algorithms that process the data and generate specific buy or sell signals. Common indicators include moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and stochastic oscillators, among others. Traders can combine multiple indicators to create more sophisticated signals, allowing algorithms to respond to various market conditions.
Effective risk management is paramount in algorithmic trading. Traders must determine the appropriate position size for each trade and establish risk limits to protect capital. Algorithms can incorporate risk management rules, such as setting stop-loss and take-profit orders, to minimize potential losses and maximize profits. Position sizing algorithms help ensure that trades align with the trader's risk tolerance and overall portfolio strategy.
Automation is the defining feature of algorithmic trading. Once the trading algorithm receives a signal to execute a trade, it automatically places the order without human intervention. Speed is critical in execution, as even slight delays can result in missed opportunities or increased slippage. Algorithms are designed to interact with trading platforms and brokers to swiftly execute orders, whether in high-frequency trading or longer-term strategies.

Developing forex algorithmic trading strategies
The foundation of successful algorithmic trading in the Forex market rests upon a well-defined trading strategy. This strategy outlines the rules and parameters that guide the algorithm's decision-making process. A clearly defined strategy helps traders maintain discipline, avoid impulsive actions, and stick to a predetermined plan even in the face of market fluctuations. It is the blueprint upon which all other components of algorithmic trading are built.
Accurate and reliable data sources are essential for crafting effective trading strategies. Traders must gather historical market data for the currency pairs they wish to trade. This data is used for in-depth analysis, allowing algorithms to identify patterns, trends, and potential entry and exit points. The quality of data and the choice of timeframes can significantly impact the strategy's performance.
Algorithm development involves translating the trading strategy into code that a computer can execute. Programmers or traders proficient in coding languages like MQL4 (for MetaTrader) or Python write the algorithms. Careful consideration must be given to the logic, rules, and conditions that govern how the algorithm will operate. Proper coding ensures the strategy is executed accurately and efficiently.
Before deploying an algorithm in a live trading environment, it should undergo rigorous backtesting. Backtesting involves running the algorithm on historical data to assess its performance. During this phase, traders can fine-tune parameters, adjust risk management rules, and optimize the strategy to maximize its profitability and minimize potential losses.
Once an algorithm has passed the backtesting phase, it is ready for real-time testing in a simulated trading environment. This allows traders to evaluate how the algorithm performs under live market conditions without risking real capital. Once the algorithm consistently demonstrates profitability and reliability, it can be deployed in the live Forex market.
Common forex algorithmic trading strategies
Algorithmic trading offers a multitude of strategies to navigate the complexities of the Forex market. Each strategy is designed to capitalise on specific market conditions and trends. Here are some common Forex algorithmic trading strategies:
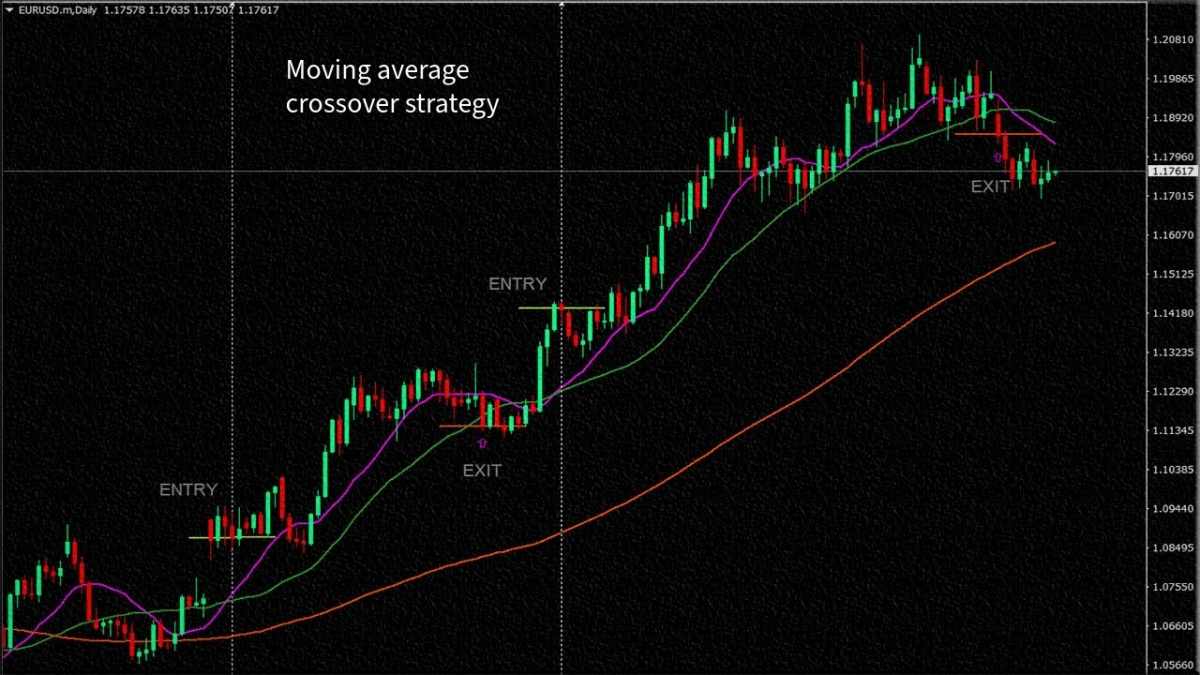
Moving average crossover strategy: This strategy involves the use of two moving averages, typically a short-term and a long-term one. When the short-term moving average crosses above the long-term moving average, it generates a buy signal, and when it crosses below, it generates a sell signal. This strategy aims to capture trend changes and exploit momentum.
Bollinger bands strategy: Bollinger Bands consist of a middle band (a simple moving average) and two outer bands that are standard deviations above and below the middle band. Traders use Bollinger Bands to identify periods of low volatility (contracting bands) and high volatility (expanding bands) to make trading decisions, such as buying during low volatility and selling during high volatility.
Relative strength index (RSI) strategy: The RSI measures the speed and change of price movements, helping traders identify overbought and oversold conditions. A common RSI strategy involves buying when the RSI is below a certain threshold (indicating oversold) and selling when it's above a threshold (indicating overbought).
Fibonacci retracement strategy: This strategy relies on the Fibonacci retracement levels, which are used to identify potential support and resistance levels based on mathematical ratios. Traders look for price reversals or trend continuation signals near these levels.
Breakout and trend-following strategies: These strategies aim to capitalize on the continuation of existing trends or the emergence of new trends. Traders identify key support and resistance levels and enter positions when price breaks through these levels, signaling a potential trend change or continuation.
Mean reversion strategy: Mean reversion strategies assume that asset prices tend to revert to their historical mean or average over time. Traders look for deviations from this mean and enter positions when they anticipate a return to the average.
Monitoring and fine-tuning strategies
Markets are dynamic, and what works today may not work tomorrow. Traders must vigilantly observe their algorithms to ensure they perform as expected. Continuous monitoring allows traders to identify potential issues, seize new opportunities, and make necessary adjustments promptly.
Even the most meticulously crafted algorithmic strategies can encounter errors. These errors may be due to data inconsistencies, coding mistakes, or unforeseen market conditions. Monitoring helps traders swiftly detect these errors and implement corrective measures to prevent losses. Common errors include order execution failures, incorrect position sizing, and data feed disruptions.
Market conditions can shift rapidly due to economic events, geopolitical developments, or shifts in sentiment. Algorithmic trading strategies that once thrived may become less effective in new market environments. Traders need to remain adaptable, constantly evaluating whether their strategies align with the current market landscape. Adaptation may involve modifying parameters, optimizing algorithms, or even developing entirely new strategies.
Fine-tuning strategies is an ongoing process to enhance performance. Traders can optimize algorithms by adjusting variables, risk management parameters, or trading timeframes. Backtesting and real-time testing are essential tools for fine-tuning, as they provide valuable insights into how adjustments impact historical and live performance.
Challenges and risks of algorithmic trading
Algorithmic trading heavily relies on accurate and timely data. Poor data quality or delays in data feeds can lead to suboptimal trading decisions and potential losses. Traders must ensure they have access to high-quality data sources and reliable infrastructure to minimize data-related challenges.
Overfitting occurs when an algorithm is excessively tailored to historical data, capturing noise rather than genuine patterns. Curve-fitting is a related risk, wherein a strategy is overly complex and fine-tuned to past performance, leading to poor results in real market conditions. Traders must strike a balance between historical performance and adaptability to avoid these pitfalls.
Algorithmic trading is not immune to market manipulation or unexpected events. Traders need to be vigilant about fraudulent activities, such as pump-and-dump schemes, and be prepared for black swan events—rare and extreme occurrences that can disrupt markets. Risk management strategies, stop-loss orders, and real-time monitoring can help mitigate these risks.
Algorithmic trading is subject to regulatory oversight in many jurisdictions, and adherence to trading rules and regulations is essential. Ethical concerns, such as the impact of high-frequency trading on market stability, also play a role. Traders must operate within legal frameworks and consider the broader ethical implications of their trading activities.
Conclusion
Developing effective algorithmic trading strategies involves a systematic approach, including data analysis, coding, backtesting, and real-time testing. Various strategies, from moving average crossovers to mean reversion, illustrate the diversity of options available to traders.
To sum up, Forex algorithmic trading strategies can help traders to effectively and accurately navigate the complex Forex market. However, traders should approach this area with caution, continuously learning and adapting to the ever-changing nature of Forex trading. By doing so, they can use the power of algorithms to boost their trading success.


